
Securely exposing web apps on Kubernetes with NGINX Ingress and Cert-manager TLS certs
Now that we have our application inside our Azure AKS up and running we want to make it available to the outside world in a secure and scalable fashion. How can we handle traffic coming towards our cluster from external facing clients? How can we intelligently and quickly route the traffic without having to deploy a ton of layer 4 load balancers.
We continue on the implementation we have discussed in the previous post Monitoring .Net Core Application with Prometheus on Azure AKS
1. Introduction
The Kubernetes ingress resource provides a simple way to configure external layer 7 load balancing for applications on Kubernetes. It functions as the entrance into our applications, the metaphorical gate. We can integrate our applications and traffic in a natural, Kubernetes-native way using the built-in ingress resource to solve common access problems and empower users to build software for handling custom traffic patterns.
The ingress controller acts as the entry point for all incoming traffic to applications running on Kubernetes. Ingress is giving your services externally-reachable urls, load balance traffic, terminate SSL, offer names based virtual hosting,etc…
The following image gives you an overview of what we will implement today:
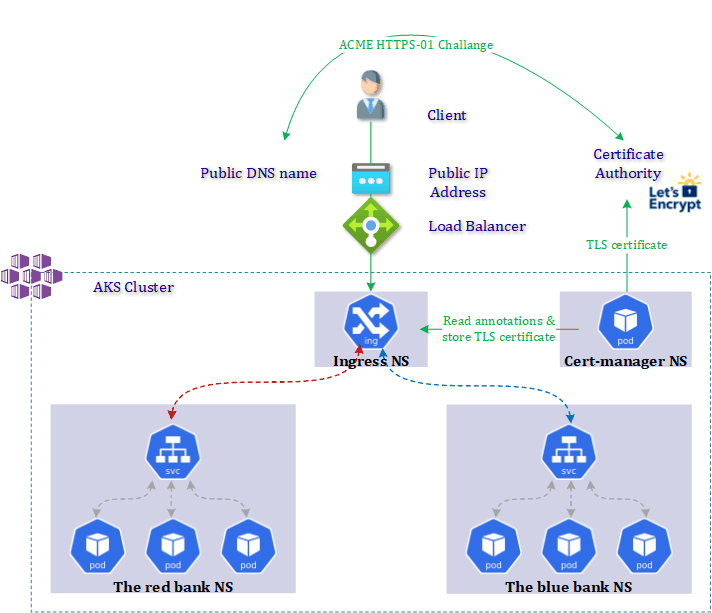
A cloud environment is by defintion extremely volatile. Luckily the creation and management of TLS certificates in a Kubernetes environment can be automated with Cert-manager to have a consistent, secure and declared-as-code machine identity protection.
Cert-manager automates the management and issuance of TLS certificates from various issuing sources. It will periodically check the validity of the certificates and will start the renewal process if necessary.
-
A ClusterIssuer represents a certificate Authority that is able to generate signed certificates by honoring certificate signing requests. A certificate is a namespaced resource that references an ClusterIssuer that determines what will be honoring the certificate request.
-
When a certificate is created, a corresponding CertificateRequest resource is created by Cert-manager containing the encoded X509 certificate request and issuer reference.
Cert-manager is using Let’s Encrypt which is a free, automated and open Certificate Authority.
Our application should be publicly accessible by routing external requests to the pods in our Kubernetes service offering a controlled network channel. Kubernetes ingress describes how to route different types of requests to different services based on predetermined set of rules.
2. Installing and configuring NGINX Ingress Controller
We start with the first Azure DevOps pipeline 1-nginx-cert-manager-pipeline.yml to install the NGINX Ingress controller and the Cert-manager charts via Helm. Automatically a public IP gets assigned to our NGINX Ingress controller which is the default behaviour in public cloud environments. If you now browse to this public IP you will land on the default “404 - No backend configured” page.
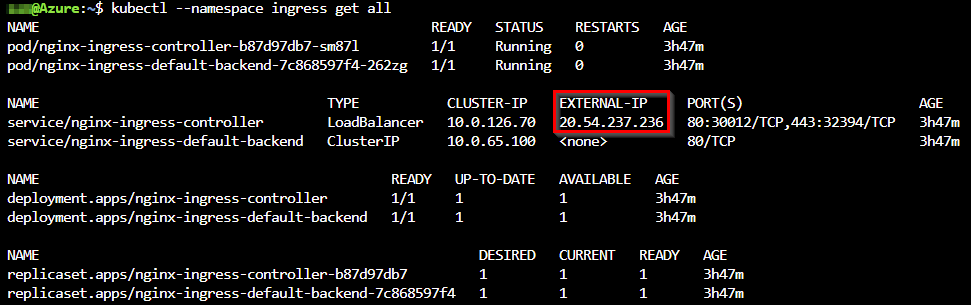
3. Setup Cert-manager with Let’s Encrypt
The deployment of Cert-manager via Helm will give us the following result:
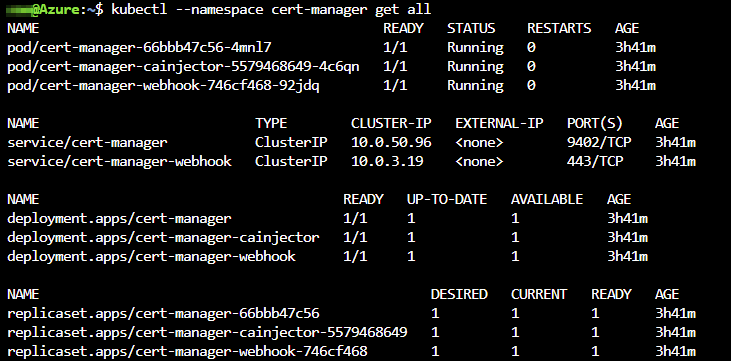
Besides these objects we also need an Issuer which is a Certificate Authority who provisions TLS certificates for a domain. We choose a ClusterIssuer which can be used cluster-wide in all namespaces.
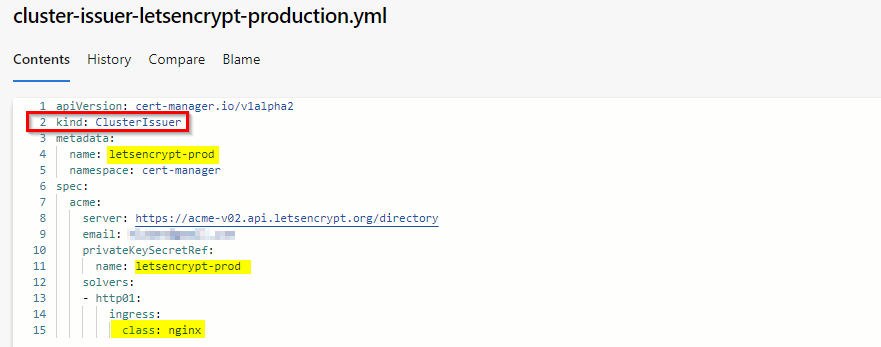
The spec.acme.privateKeySecretKeyRef is the Kubernetes secret used to store the ACME account private key that Cert-manager creates for us.
Cert-manager will create custom resources to issue a certificate, orders and challenges.
$ kubectl get challenges, orders
$ kubectl describe challenge <insert challenge-name>
$ kubectl describe order <insert order-name>
Use the following commands to view the outcome:
$ kubectl get clusterissuer,certificates --all-namespaces
$ kubectl describe certificate thebank-ingress.westeurope.cloudapp.azure.com -n thebank
4. Deploy Kubernetes ingress
We re-use the Azure DevOps pipeline 2-thebank-app-pipeline.yml from our previous blogpost. Additionally we add a pipeline-task to deploy the Kubernetes ingress manifest for our application in the application namespace.
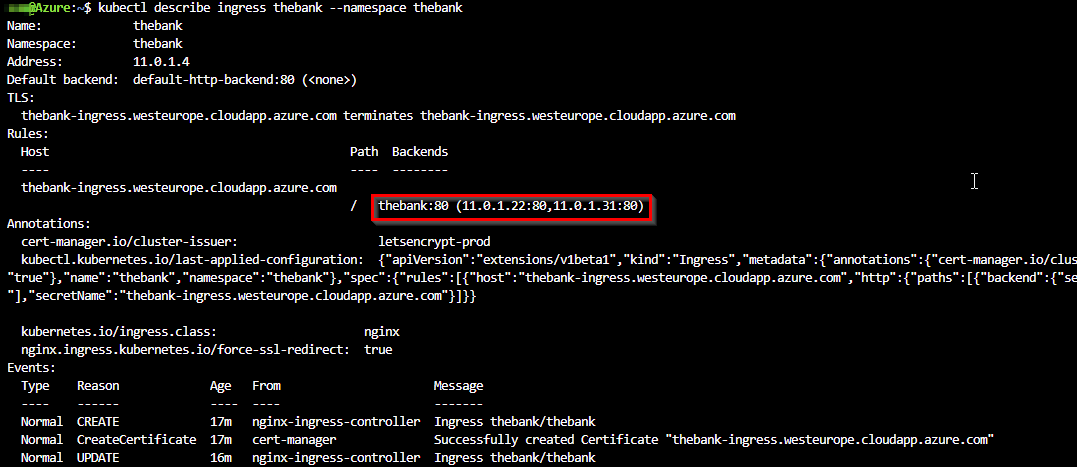
The Kubernetes annotation nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: “true” in the ingress manifest will redirect traffic from http to https when TLS is enabled on the ingress.
We specify in the annotation also the ingress.class to nginx to make sure that this ingress can only be served by our NGINX ingress controller. The spec.tls.secretName is the Kubernetes secret to store the certificate received from Let’s Encrypt.
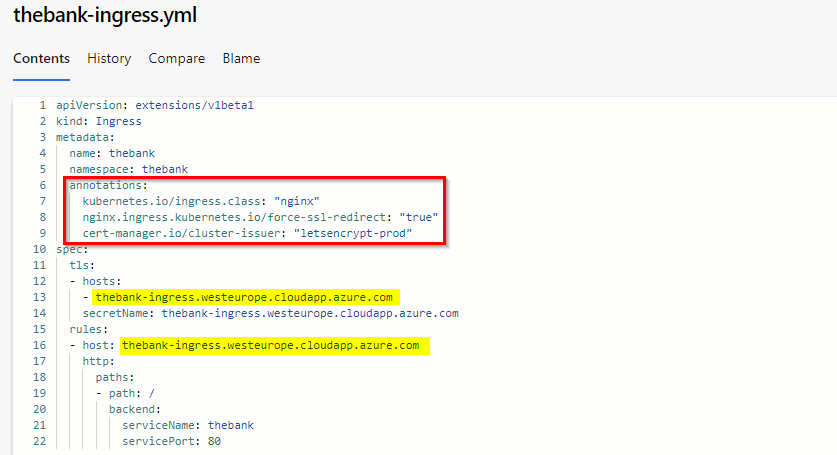
The end-result gives us a TLS secured website with a valid certificate.
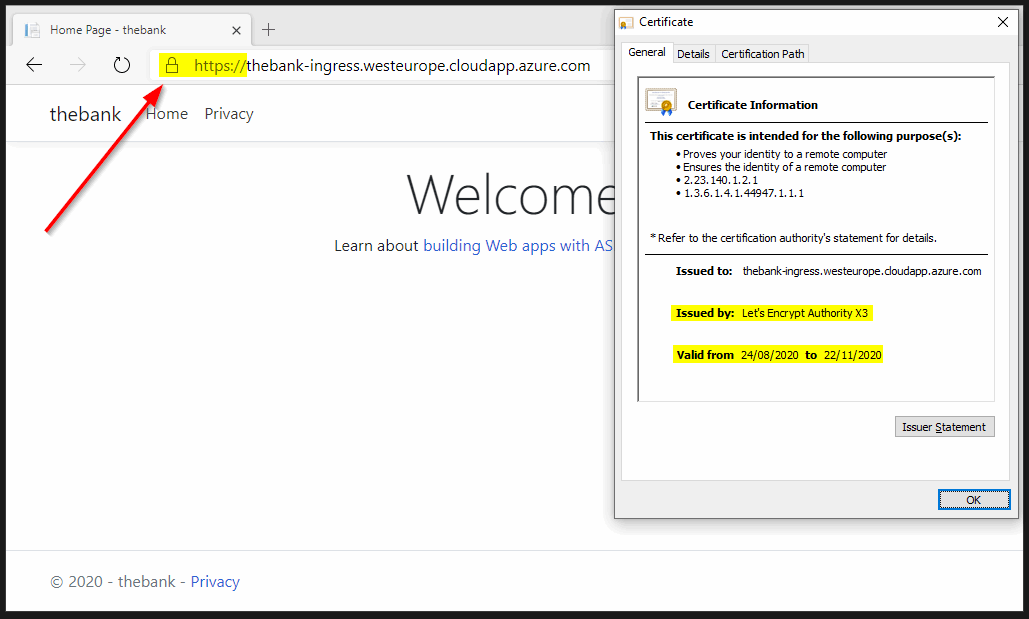
4.1 TLS verification
Let’s verify with SSL Labs to identify we are in good shape for our TLS implementation.
5. Troubleshooting tips
5.1 Check NGINX configuration
We can verify the NGINX config file inside the NGINX controller pod.
$ kubectl exec -it -n ingress nginx-ingress-controller-f4979b754-pn6ld /bin/bash
bash-5.0$ cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep -A 10 thebank
5.2 Verify NGINX container logs
The log file of the NGINX Ingress controller will give you more information about the applied Ingress rules.
$ kubectl logs -n ingress nginx-ingress-controller-f4979b754-pn6ld
5.3 Kubernetes service reachability within the cluster
To exclude Kubernetes service misconfiguration, we access the NGINX ingress controller and try to reach our application service on the internal port.
$ kubectl exec -it -n ingress nginx-ingress-controller-f4979b754-pn6ld /bin/bash
bash-5.0$ curl 10.0.207.9
5.4 Verify Cert-manager container logs
The log file of the Cert-manager will give you more info about the certificate process.
$ kubectl --namespace cert-manager logs -l app=cert-manager -c cert-manager
The configuration we used in this post can be found on https://github.com/dewolfs/kubernetes-nginx-certs.